The CMA certification landscape is experiencing unprecedented growth, with employment of medical assistants projected to grow 15 percent from 2023 to 2033, much faster than the average for all occupations, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. This explosive demand creates exceptional opportunities for those who understand how to become a CMA strategically.
I’ve watched countless professionals stumble through the certification process, making costly mistakes that could have been avoided with proper planning. The truth is, most people pursuing CMA certification don’t realize they’re choosing between two completely different career trajectories, and this confusion creates planning disasters that waste months of preparation time and thousands of dollars.
The Identity Crisis: Medical vs. Management CMA
Most people pursuing cma certification don’t realize they’re choosing between two completely different career trajectories. The medical assistant route focuses on clinical skills and patient care, while the management accountant path centers on financial analysis and business strategy. This fundamental confusion creates planning disasters that can waste months of preparation time and thousands of dollars in misdirected efforts.
The acronym “CMA” creates immediate confusion because both certifications use identical letters but serve entirely different industries with separate governing bodies, exam structures, and career outcomes. I’ve seen professionals spend weeks studying financial analysis materials when they actually wanted to work in healthcare settings, or vice versa.
Career planning becomes impossible when you’re preparing for the wrong certification type, leading to misaligned study materials, inappropriate work experience, and unsuitable educational prerequisites. The first step in your certification journey must be crystal clear identification of which path aligns with your career goals.
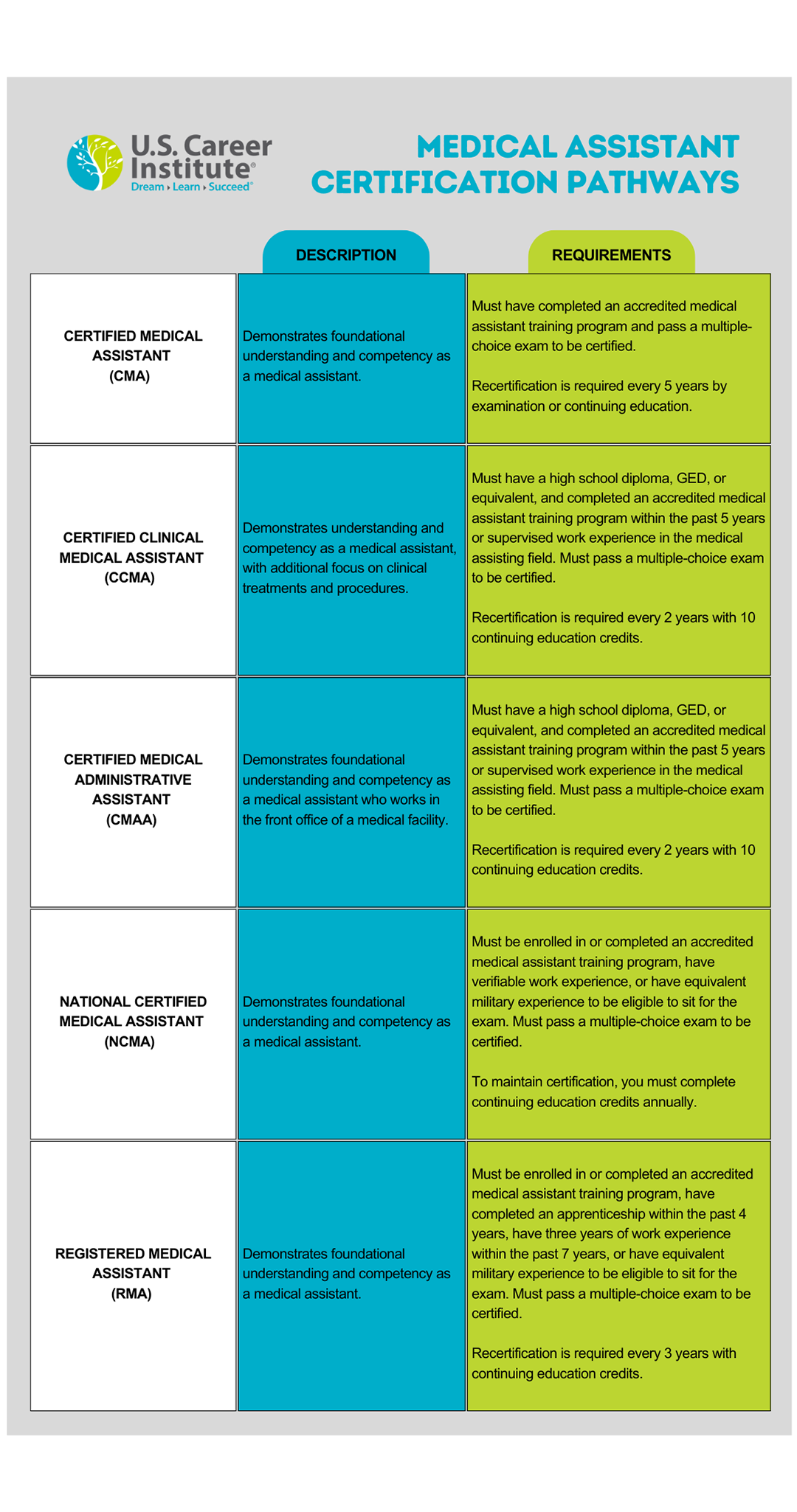
Understanding the Medical Assistant Certification Landscape
The medical assistant certification world contains multiple pathways that aren’t immediately obvious to newcomers. You’ll encounter CCMA, CMA, RMA, and other acronyms that represent different certifying organizations with varying requirements, recognition levels, and career implications. Each pathway offers distinct advantages depending on your current situation, geographic location, and career timeline.
Different certifying bodies (AAMA, NHA, AMT) maintain separate eligibility requirements, with some accepting online education while others require accredited programs from specific institutions. This variation means you could qualify for one certification but not another, even with identical educational backgrounds.
Employer recognition varies significantly by region and healthcare system, making research into local preferences essential before committing to a specific certification pathway. What works in California might not be recognized in Texas, and what hospitals prefer might differ from what private practices value.
Certification maintenance requirements differ substantially between organizations, affecting long-term career costs and continuing education obligations. Some require annual fees and continuing education, while others have different renewal cycles and requirements.
Understanding the distinction between various credentials becomes crucial when evaluating whether certificates qualify as degrees, as many medical assistant programs offer certificates rather than traditional degree pathways.
The healthcare industry continues to evolve rapidly, with new regulations and technology implementations changing the role of medical assistants across different healthcare settings. Industry experts emphasize that “Certified Management Accountants focus on areas like strategic financial management, financial planning, analysis, cost management, and risk management” according to Kansas City career guidance resources, highlighting the strategic nature of management accounting roles.
|
Certification Type |
Governing Body |
Exam Frequency |
Education Requirements |
Experience Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Medical Assistant (AAMA) |
American Association of Medical Assistants |
3 times per year |
CAAHEP/ABHES accredited program |
None required |
|
Clinical Medical Assistant (NHA) |
National Healthcareer Association |
Year-round |
Various pathways accepted |
1 year or formal training |
|
Registered Medical Assistant (AMT) |
American Medical Technologists |
Year-round |
Accredited program or experience |
Varies by pathway |
|
Management Accountant (IMA) |
Institute of Management Accountants |
Year-round |
Bachelor’s degree |
2 years professional experience |
Why CCMA Might Be Your Better Starting Point
The Certified Clinical Medical Assistant (CCMA) certification through the National Healthcareer Association often provides faster entry into the medical assistant field compared to traditional CMA routes. CCMA requirements typically include more flexible educational pathways and shorter waiting periods, making it attractive for career changers or those needing immediate employment opportunities.
CCMA eligibility includes completion of medical assistant programs, military medical assistant training, or one year of supervised work experience, providing multiple entry points for different backgrounds. This flexibility means you might already qualify without additional education.
The certification exam can be scheduled more frequently than AAMA’s CMA exam, which is only offered during specific testing windows throughout the year. When you’re ready to test, you don’t want to wait months for the next available exam date.
Many employers recognize CCMA credentials equally to certified medical assistant certification, but verification of local market acceptance is crucial before making this choice. CCMA certification costs are typically lower than certified medical assistant certification, including both exam fees and preparation materials, making it more accessible for budget-conscious candidates.
When considering different certification pathways, professionals often need to understand how to obtain their college transcripts for verification purposes, as medical assistant certification programs require documented educational backgrounds.
Sarah, a military veteran with medical corps experience, chose the CCMA pathway because her military training qualified her for immediate certification without additional formal education. She scheduled her exam within two weeks of application and began working as a certified medical assistant within a month, while her civilian counterparts waited months for AAMA testing windows.
Navigating Medical Assistant Certification Programs
Medical assistant certification programs vary dramatically in quality, accreditation status, and preparation focus. Some programs prepare you specifically for AAMA certification, others target NHA credentials, and many don’t clearly specify their alignment. This misalignment can leave you prepared for the wrong exam or inadequately prepared for your chosen certification path.
Program accreditation by CAAHEP or ABHES is required for AAMA certified medical assistant eligibility, but many programs advertise medical assistant training without meeting these specific accreditation standards. You could complete an entire program only to discover you don’t qualify for your intended certification.
Online programs may not qualify you for certain certifications, particularly AAMA’s certified medical assistant, which requires hands-on clinical experience that online formats cannot provide. Program length and clinical hour requirements vary significantly, with some offering accelerated tracks that may not meet all certification body requirements.
Financial aid availability and job placement assistance differ substantially between programs, affecting both your educational investment and post-graduation employment prospects.
The Certified Management Accountant Path
The management accountant CMA certification requires a bachelor’s degree, two years of professional experience, and passing a comprehensive two-part examination. This certified management accountant path targets finance and accounting professionals seeking advancement in corporate environments, consulting roles, or specialized financial analysis positions. The requirements are significantly more rigorous than medical assistant certifications.
The bachelor’s degree requirement must be from an accredited institution, with specific coursework in accounting, finance, or business administration preferred but not always required. Professional experience must be in management accounting or financial management roles, with specific documentation requirements that many candidates underestimate.
The two-part exam covers financial planning, analysis, control, and decision support, requiring deep understanding of advanced accounting principles and business strategy. The certified management accountant examination requires candidates to achieve at least 360 out of 500 possible points to pass, with both parts combined to determine overall success, according to Becker CMA Exam Requirements. This scoring system allows for strategic preparation focusing on stronger areas while maintaining minimum competency across all topics.
Building Your Academic Credentials
Many certified management accountant candidates discover too late that their educational documentation is insufficient, incomplete, or difficult to verify. Proper academic credential preparation involves more than just having a degree – you need official transcripts, course descriptions, and sometimes additional documentation to prove your educational foundation meets certification requirements.
Official transcripts must be sent directly from educational institutions to the certification body, with unofficial copies or student-provided documents being unacceptable for verification purposes. Course descriptions may be required to demonstrate that your degree program included sufficient accounting and business coursework, particularly for degrees in non-business fields.
Grade point average requirements may apply, with some certification bodies requiring minimum GPA levels that aren’t always clearly communicated in initial application materials. Documentation of any academic honors, certifications, or additional coursework can strengthen your application and potentially reduce experience requirements in some cases.
Professional certification candidates frequently encounter challenges when obtaining diplomas from closed schools, requiring alternative documentation strategies to meet CMA certification requirements.
Strategic Work Experience Planning
The two-year professional experience requirement can be fulfilled through various pathways including full-time employment, part-time work, internships, and volunteer positions in qualifying roles. Strategic planning of this experience requirement can significantly accelerate your CMA certification timeline and strengthen your overall professional profile.
Experience must be in management accounting or financial management roles, with specific job function documentation required to prove relevance to certification requirements. Part-time experience can count toward the requirement but may need to be calculated differently, with some certification bodies requiring longer time periods to accumulate equivalent experience.
Internships and entry-level positions may qualify if they include appropriate management accounting responsibilities, making early career planning crucial for certification timeline optimization. Documentation requirements include detailed job descriptions, supervisor verification, and sometimes performance evaluations to prove the quality and relevance of your professional experience.
Beyond Study Guides: Mental Preparation
The certified management accountant exam’s 50% pass rate reflects psychological barriers as much as knowledge gaps. Mental preparation involves developing test-taking strategies, managing exam anxiety, building confidence through practice, and creating sustainable study habits that maintain motivation throughout the lengthy preparation period.
Exam anxiety management techniques specific to high-stakes professional certifications can improve performance regardless of knowledge level, including breathing exercises, visualization, and stress reduction strategies. Time management during the actual exam requires practice with timed simulations that replicate the pressure and format of the real testing environment.
Confidence building through incremental progress tracking helps maintain motivation during the months-long preparation period when progress can feel slow or inconsistent. Recovery strategies for handling difficult questions or sections during the exam prevent panic responses that can derail performance on subsequent questions.
The Hidden Credentialing Challenges
Documentation and verification hurdles represent the most overlooked aspect of CMA certification pursuit. Missing educational records, closed institutions, international credential complications, and verification delays can derail even the most prepared candidates. These administrative challenges often prove more difficult to overcome than the actual knowledge requirements for certification.
Educational institutions that have closed, merged, or changed ownership create verification nightmares that can delay certification applications by months or years. International educational credentials require additional verification steps through specialized agencies that many candidates don’t discover until deep into the application process.
Educational Record Requirements
Both medical assistant and management CMA paths require verified educational credentials, but the specific requirements vary significantly between certification bodies. Understanding exactly what documentation you need, how to obtain it, and what alternatives exist when standard verification fails can save months of delays and frustration.
Transcript verification requirements differ between certification bodies, with some accepting electronic transcripts while others require sealed paper documents sent directly from institutions. Course-by-course evaluations may be necessary for degrees from non-accredited institutions or international schools, adding time and cost to the verification process.
Alternative documentation options exist when standard transcripts are unavailable, including diploma verification, course catalogs, and third-party verification services that specialize in difficult cases.
When Educational Records Go Missing
Educational institutions close, merge, or lose records more frequently than most people realize. When your school no longer exists or cannot locate your records, you face verification challenges that can completely halt your certification progress. Understanding your options and acting quickly can prevent these situations from becoming permanent roadblocks.
Closed institution records are often transferred to state education departments or surviving institutions, but tracking down these transfers requires detective work that can take weeks or months. Alternative verification methods include contacting former classmates, professors, or administrators who may have retained records or can provide verification letters.
Third-party verification services specialize in difficult cases and may have access to archived records or alternative verification methods that individuals cannot access. Backup documentation should be obtained immediately upon graduation, including multiple official transcripts, course catalogs, and degree verification letters stored in secure locations.
When traditional verification methods fail, professionals may need to consider replacement diplomas as interim documentation while pursuing official verification through alternative channels.
When Maria’s community college closed five years after her graduation, she discovered the records had been transferred to the state education department. However, the transfer was incomplete, missing her final semester grades. She successfully obtained verification by contacting her former academic advisor who had retained personal copies of student records, demonstrating the importance of maintaining professional relationships and exploring alternative verification sources.
Foreign Education Verification
Candidates with international educational backgrounds face additional verification steps that are rarely discussed in standard CMA certification preparation materials. These requirements can add months to your certification timeline and significant costs to your budget if not planned properly from the beginning of your certification journey.
Credential evaluation services must be approved by your chosen certification body, with different organizations accepting different evaluation agencies. Document translation requirements are specific and costly, often requiring certified translators and notarized copies that must be obtained in particular sequences.
Processing times for international credential evaluation can extend 8-12 weeks during busy periods, making early submission crucial for meeting certification deadlines.
Third-Party Verification Services
Understanding which credential evaluation services are accepted by certification bodies can save significant time and money in the application process. Different services specialize in different regions, offer varying levels of detail, and charge different fees for similar services.
WES, ECE, and other major evaluation services have different strengths in evaluating credentials from specific countries or educational systems. Course-by-course evaluations provide more detailed analysis than general evaluations but cost significantly more and take longer to complete.
Some certification bodies accept only specific evaluation services, making research into accepted providers essential before beginning the evaluation process. Rush processing options are available but can double or triple evaluation costs, making early planning financially advantageous.
Document Authentication Protocols
Foreign documents require specific translation and notarization procedures that must be completed before the certification application can proceed. These requirements are technical, sequential, and unforgiving – missing a step often means starting the entire process over.
Document authentication must follow specific sequences, with original documents often requiring apostille certification from the issuing country before translation. Certified translation services must be approved by certification bodies, with different organizations maintaining different lists of acceptable translators.
Notarization requirements vary by document type and issuing country, with some documents requiring multiple levels of authentication before acceptance. Processing timelines for authentication can extend several months when multiple countries and agencies are involved, making early initiation crucial for meeting certification deadlines.
The Strategic Career Positioning Approach
The timing of when you pursue CMA certification can significantly impact your career trajectory and earning potential. Most professionals treat certification as a checkbox activity rather than a strategic career move. Smart timing can position you ahead of competitors, unlock employer funding, and create opportunities for rapid advancement that wouldn’t exist otherwise.
Market conditions and industry demand cycles affect the value of newly certified professionals, with timing your certification completion to coincide with peak hiring periods maximizing job opportunities. Internal promotion cycles within organizations often align with budget planning periods, making certification completion timing crucial for capturing advancement opportunities.
Certification as a Career Accelerator
Understanding how to leverage certification timing can position you ahead of competitors and create opportunities for rapid career advancement. Rather than pursuing certification in isolation, successful professionals integrate their certification journey with broader career planning, networking activities, and skill development initiatives.
Certification announcement timing within your current organization can trigger promotion discussions, salary negotiations, and new responsibility assignments if handled strategically. Industry networking during certification pursuit creates professional relationships that often lead to job opportunities before certification completion.
Skill demonstration throughout the certification process can showcase your commitment and capabilities to current supervisors, leading to increased responsibilities and advancement opportunities. With approximately 119,800 openings for medical assistants projected each year on average over the decade, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, strategic timing of certification completion can position candidates to capture these opportunities during peak hiring periods.
Negotiating Certification Support
Many employers will fund certification efforts if approached strategically, but this requires understanding how to present the business case effectively. Employer support can include exam fees, study materials, paid study time, and salary increases upon certification completion.
Business case development should focus on specific organizational benefits rather than personal career advancement, including improved efficiency, reduced errors, and enhanced compliance capabilities. Timing requests with budget cycles and performance review periods increases approval likelihood, as managers have clearer pictures of available funding and your performance value.
Commitment agreements often accompany employer funding, requiring you to remain with the organization for specific periods after certification completion. Multiple funding sources can be combined, including employer reimbursement, professional development budgets, and tax deduction strategies to minimize personal financial investment.
|
Funding Source |
Typical Coverage |
Requirements |
Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Employer Reimbursement |
50-100% of costs |
Passing grade, employment commitment |
After completion |
|
Professional Development Budget |
Up to annual limit |
Manager approval, relevance to role |
Before or after |
|
Tax Deductions |
25-40% of costs |
Documentation, job relevance |
Following tax year |
|
Professional Associations |
Scholarships/grants |
Membership, application process |
Varies |
Post-Certification Career Mapping
The real value of CMA certification emerges in how you leverage it for specialized career paths that aren’t immediately obvious to most professionals. Certification opens doors to niche markets, consulting opportunities, and specialized roles that offer higher compensation and job security than traditional positions.
Specialized industry sectors often pay premium rates for certified professionals, including healthcare administration, government contracting, and regulatory compliance roles. Geographic arbitrage opportunities exist where certified professionals can command higher salaries in underserved markets or remote work arrangements.
Certification can serve as a foundation for additional credentials and specializations that create compound career advantages over time.
Finding Underserved Professional Segments
CMA certification opens doors to specialized roles in healthcare administration, forensic accounting, and regulatory compliance that offer higher compensation and job security. These niche markets often have less competition and higher demand than traditional accounting or medical assistant positions.
Healthcare administration roles increasingly require both clinical understanding and financial expertise, creating opportunities for professionals with medical assistant backgrounds who pursue additional business education. Forensic accounting and fraud investigation roles value the detailed analytical skills developed through CMA certification preparation, often offering significantly higher compensation than traditional accounting positions.
Regulatory compliance positions in healthcare and financial services sectors require the systematic thinking and attention to detail that CMA certification demonstrates. Government contracting opportunities often prefer or require certified professionals, providing job security and benefits packages that exceed private sector offerings.
James leveraged his medical assistant CMA certification to transition into healthcare administration by pursuing additional coursework in healthcare finance. His unique combination of clinical knowledge and financial certification qualified him for a hospital compliance officer position with a 40% salary increase and comprehensive benefits package that included continuing education funding.
The Psychological and Practical Preparation Framework
Success in CMA certification depends as much on psychological preparation and practical life management as it does on academic knowledge. Traditional approaches underestimate these factors, leading to high failure rates despite adequate knowledge preparation. Mental conditioning, stress management, and sustainable study practices often determine certification success more than raw intelligence or prior experience.
Psychological barriers including imposter syndrome, test anxiety, and perfectionism can sabotage well-prepared candidates during crucial exam moments. Life management skills including time allocation, family communication, and work-study balance directly impact study effectiveness and retention rates.
Long-Term Learning Strategies
Traditional cramming approaches fail for CMA certification due to the breadth of material and practical application requirements. Successful candidates develop sophisticated learning approaches that integrate spaced repetition, practical application, and stress management techniques over extended preparation periods.
Material breadth requires systematic coverage over months rather than weeks, with retention strategies that prevent early material from being forgotten while learning new concepts. Practical application integration helps cement theoretical knowledge while building real-world skills that enhance both exam performance and job effectiveness.
Sustainable pace management prevents burnout while maintaining consistent progress toward certification goals.
Memory Retention Optimization
Implementing scientifically-backed spaced repetition techniques can improve retention rates by up to 200% compared to traditional study methods. These techniques require initial setup time but dramatically reduce total study hours needed while improving long-term knowledge retention.
Spaced repetition algorithms determine optimal review timing for individual concepts based on your personal retention patterns and difficulty levels. Digital flashcard systems can automate spaced repetition scheduling while tracking your progress and identifying persistent knowledge gaps.
Active recall techniques during spaced repetition sessions strengthen memory formation more effectively than passive review methods. Integration with daily routines makes spaced repetition sustainable over the months-long preparation period required for comprehensive CMA certification preparation.
Real-World Skill Development
The most successful CMA certification candidates integrate certification study with actual workplace challenges, creating a feedback loop that enhances both learning and job performance. This approach transforms study time from academic exercise into practical skill building that provides immediate career benefits.
Workplace application opportunities allow you to practice certification concepts in real situations, reinforcing learning while demonstrating value to current employers. Case study development from your own work experiences creates personalized study materials that are more memorable and relevant than generic textbook examples.
Skill demonstration during the certification process can lead to increased responsibilities and recognition before certification completion. Problem-solving practice with real workplace challenges builds confidence and practical expertise that translates directly to exam performance.
Maintaining Performance Under Pressure
Developing stress management techniques specific to high-stakes professional examinations can be the difference between passing and failing, regardless of knowledge level. These techniques must be practiced and refined during preparation rather than attempted for the first time during the actual exam.
Breathing techniques and physical relaxation methods can be practiced during study sessions and deployed during exam situations to maintain focus and reduce anxiety. Cognitive reframing strategies help transform exam pressure into performance enhancement rather than performance degradation.
Practice testing under simulated pressure conditions builds familiarity with stress responses and develops coping mechanisms specific to exam environments. Recovery protocols for handling difficult questions prevent panic responses that can cascade into broader exam performance problems.
Certified management accountants must complete 30 hours of continuing professional education (CPE) per year, including two hours of ethics courses, to maintain their certification according to Becker’s CMA requirements guide. This ongoing commitment requires sustainable learning habits developed during initial certification preparation.
Building Your Professional Network
CMA certification success often depends on having the right support system in place, including mentors, study groups, and professional connections that extend beyond the certification process. These relationships provide accountability, knowledge sharing, and career opportunities that multiply the value of your certification investment.
Study group formation with other certification candidates creates accountability systems and knowledge sharing opportunities that improve everyone’s preparation effectiveness. Mentor relationships with already-certified professionals provide insider knowledge about exam strategies, career positioning, and industry insights not available through formal study materials.
Professional association participation during certification pursuit builds networks that provide job opportunities, continuing education resources, and career advancement support throughout your professional life. Professional networking often requires demonstrating your educational credentials, making it essential to understand how academic transcripts work for verification purposes during CMA certification applications.
The Technology Integration Revolution
The certification landscape is rapidly evolving with AI-powered study tools, virtual reality simulations, and blockchain credential verification. These technological advances create new opportunities for tech-savvy candidates while potentially disadvantaging traditional learners who don’t adapt to new learning methods and verification systems.
AI-powered study platforms can analyze learning patterns and optimize study schedules in ways that human planning cannot match, but require comfort with technology and data sharing. Blockchain verification systems are beginning to revolutionize credential storage and verification, potentially eliminating traditional transcript challenges while creating new technical requirements.
Machine Learning Study Optimization
Advanced algorithms can now analyze your learning patterns, identify knowledge gaps, and create personalized study schedules that adapt in real-time to your progress and retention rates. These systems provide unprecedented customization but require consistent data input and technology comfort to maximize effectiveness.
Learning analytics platforms track thousands of micro-interactions during study sessions, providing insights into optimal study times, material difficulty rankings, and knowledge retention patterns. Adaptive questioning systems adjust difficulty levels and topic focus based on your performance patterns, ensuring efficient use of study time while maintaining appropriate challenge levels.
Predictive modeling can estimate exam readiness weeks before test day, allowing for strategic adjustment of study focus and exam scheduling.
Data-Driven Certification Success
Modern platforms track thousands of micro-interactions during study sessions, providing insights into optimal study times, material difficulty rankings, and probability of exam success weeks before test day. This data-driven approach removes guesswork from certification preparation while requiring comfort with detailed performance tracking.
Performance analytics identify specific knowledge gaps and learning inefficiencies that traditional study methods cannot detect, allowing for targeted improvement efforts. Optimal timing analysis reveals when you learn most effectively, enabling study schedule optimization that maximizes retention while minimizing total study hours.
Readiness assessment algorithms provide objective measures of exam preparedness, reducing anxiety while ensuring adequate preparation before test scheduling. Comparative analysis against successful candidates reveals study patterns and strategies that correlate with certification success.
Immersive Medical Assistant Preparation
VR technology now allows medical assistant candidates to practice procedures in risk-free virtual environments, building muscle memory and confidence before entering real clinical settings. This technology bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application in ways that traditional education cannot provide.
Virtual patient interactions allow unlimited practice with diverse scenarios and patient types without scheduling constraints or patient availability limitations. Procedure simulation provides immediate feedback on technique and accuracy, accelerating skill development while preventing the formation of bad habits.
Risk-free environment enables learning from mistakes without patient safety concerns or supervisor judgment, encouraging experimentation and confidence building. Standardized scenarios ensure consistent training experiences while allowing for repeated practice of challenging procedures until mastery is achieved.
Decentralized Certification Verification
Emerging blockchain technologies are beginning to revolutionize how professional credentials are stored, verified, and transferred between institutions. These systems potentially eliminate traditional transcript verification challenges while creating new technical requirements and adoption barriers.
Blockchain credential storage provides tamper-proof verification that eliminates fraud concerns while enabling instant verification by employers and certification bodies. Smart contract automation can streamline certification renewal processes and continuing education tracking, reducing administrative overhead for both professionals and certifying organizations.
Global credential portability enables seamless international recognition of certifications, opening career opportunities previously limited by geographic verification challenges.
Automated Credential Verification
Smart contracts can automatically verify educational requirements, work experience, and continuing education credits, streamlining the certification renewal process and reducing administrative overhead. This automation requires initial setup but eliminates ongoing verification delays and documentation challenges.
Automated verification systems can instantly confirm credential authenticity without human intervention, eliminating processing delays and reducing verification costs. Continuing education tracking becomes seamless when integrated with blockchain systems, automatically updating certification status as requirements are completed.
Multi-party verification enables complex credential requirements to be verified simultaneously across multiple institutions and organizations. Fraud prevention becomes inherent in blockchain systems, eliminating concerns about falsified credentials or documentation.
Cross-Border Professional Recognition
Blockchain-based credentials enable seamless international recognition of certifications, opening global career opportunities previously limited by geographic credential transfer challenges. This technology particularly benefits professionals with international backgrounds or those seeking global career mobility.
International credential transfer becomes instantaneous when both issuing and receiving organizations participate in blockchain verification networks. Language barriers are reduced when credential information is stored in standardized digital formats that can be automatically translated.
Regulatory compliance across different countries becomes more manageable when credential information is stored in formats that meet multiple jurisdictional requirements. Career mobility increases dramatically when professionals can instantly verify their credentials in any participating country or organization.
The Economic Intelligence Factor
Understanding the complete economic ecosystem surrounding CMA certification reveals hidden costs, unexpected revenue streams, and strategic financial planning opportunities. The true financial impact extends far beyond certification fees and salary increases to include tax advantages, insurance benefits, and wealth-building strategies that can transform certification from an expense into an investment vehicle.
Hidden costs including continuing education, renewal fees, and professional development can significantly impact the total cost of certification over time. Revenue opportunities through consulting, training, and specialized services can generate returns that far exceed traditional employment salary increases.
Comprehensive Financial Impact Analysis
The true return on investment for CMA certification extends far beyond salary increases, encompassing tax advantages, insurance benefits, retirement planning opportunities, and wealth-building strategies. Understanding these broader financial implications enables strategic decision-making that maximizes certification value.
Tax optimization strategies can offset 25-40% of certification costs through professional development deductions, continuing education expenses, and business-related travel. Insurance benefits including reduced professional liability premiums and expanded coverage options create ongoing financial advantages that compound over time.
Retirement planning opportunities through professional associations and specialized investment options can accelerate wealth building for certified professionals.
Certification-Related Deductions
Professional certification expenses, including study materials, exam fees, and continuing education, often qualify for significant tax deductions that can offset 25-40% of total certification costs. Strategic timing and documentation of these expenses can maximize tax benefits while supporting certification goals.
Educational expense deductions apply to certification-related costs when they maintain or improve skills required for your current job or meet employer requirements. Professional development expenses including conference attendance, networking events, and continuing education can be deducted when directly related to certification maintenance.
Home office deductions may apply when space is used exclusively for certification study, providing additional tax benefits for dedicated study areas. Documentation requirements for tax deductions are specific and must be maintained throughout the certification process to support deduction claims.
Professional Liability Benefits
Certified professionals typically qualify for lower professional liability insurance premiums and expanded coverage options, creating ongoing financial benefits that compound over time. These insurance advantages often offset certification costs within the first few years while providing enhanced protection throughout your career.
Premium reductions for certified professionals can range from 10-25% annually, creating substantial savings over the course of a career. Coverage enhancements available to certified professionals include higher liability limits and broader protection scope at comparable costs to basic coverage for non-certified professionals.
Group insurance options through professional associations provide additional savings and specialized coverage options not available to individual purchasers. Risk assessment improvements from certification training can further reduce insurance costs while improving professional practice quality.
Business Development Through Credentials
CMA certification can serve as a foundation for consulting practices, training businesses, and specialized service offerings that generate revenue streams independent of traditional employment. These entrepreneurial opportunities often provide higher income potential and greater professional flexibility than conventional career paths.
Consulting practice development leverages certification credibility to attract clients willing to pay premium rates for specialized expertise. Training and education services can generate passive income streams through online courses, certification preparation programs, and professional development workshops.
Specialized service offerings in niche markets often command higher rates and face less competition than general practice areas.
Independent Professional Services
Certified professionals can command premium rates for specialized consulting services, often earning 2-3 times their employed counterparts while maintaining flexible schedules and diverse client portfolios. Building a consulting practice requires business development skills but offers significant income and lifestyle advantages.
Premium rate justification becomes easier with certification credentials, as clients perceive certified professionals as more competent and trustworthy. Client acquisition strategies for certified professionals include leveraging professional networks, association memberships, and referral systems that non-certified competitors cannot access.
Service specialization opportunities emerge from certification knowledge, allowing focus on high-value niche markets with less competition and higher profit margins. Business structure optimization for consulting practices can provide tax advantages and liability protection while supporting professional growth.
Knowledge Monetization Strategies
Experienced CMAs can develop training programs, online courses, and certification preparation services, creating passive income streams that leverage their expertise and certification journey. These knowledge-based businesses scale efficiently while providing valuable services to other professionals.
Online course development transforms certification knowledge into scalable products that generate revenue without ongoing time investment. Certification preparation services leverage your successful certification experience to help other candidates, creating recurring revenue through coaching and tutoring services.
Professional speaking opportunities at conferences and industry events provide additional income while building professional reputation and network connections. Content creation including books, articles, and digital resources can generate ongoing royalties while establishing thought leadership in your field.
Many professionals exploring entrepreneurial opportunities discover they need backup documentation for business licensing, making services like academic document replacement valuable for maintaining professional credentials during business development.
The evolving professional landscape continues to create new opportunities for certified professionals, with industry recognition expanding across multiple sectors. As noted in recent career development resources, “The Institute of Management Accountants rules over the CMA credential and is globally recognized in the finance and accounting industry” Kansas City career guidance, emphasizing the international recognition and career mobility that certification provides.
When you need reliable backup documentation to support your CMA certification journey, ValidGrad provides professional replacement documents that ensure administrative challenges don’t derail your career progress. Whether you’re dealing with closed institutions, lost transcripts, or international credential verification delays, having backup documentation readily available demonstrates professional preparedness while keeping your certification timeline on track.
Final Thoughts
Your CMA certification journey represents more than acquiring credentials – it’s about strategically positioning yourself for long-term career success. The path requires careful planning, psychological preparation, and understanding of both obvious and hidden challenges that can impact your timeline and outcomes.
Success depends on choosing the right certification type for your career goals, preparing for documentation challenges before they arise, and leveraging technology and financial strategies that maximize your investment return. The professionals who thrive are those who treat certification as part of a broader career strategy rather than an isolated achievement.
The certification landscape continues evolving with new technologies, verification methods, and career opportunities. Staying informed about these changes while maintaining focus on fundamental preparation principles will serve you well throughout your professional journey.
Strategic certification planning requires understanding both immediate requirements and long-term career implications, with decisions made based on comprehensive analysis rather than convenience or cost alone. Documentation preparation should begin early in your certification journey, with backup plans and alternative verification methods identified before they become necessary.
Technology integration and financial optimization strategies can significantly enhance certification value while reducing costs and time investment. Professional network development during certification pursuit creates lasting relationships that provide ongoing career benefits far beyond the certification itself.
CMA Certification Readiness Checklist
Pre-Application Phase:
-
☐ Identify correct CMA certification type (Medical Assistant vs Management Accountant)
-
☐ Research local employer preferences for certification bodies
-
☐ Obtain multiple official transcripts from all educational institutions
-
☐ Verify educational institution accreditation status
-
☐ Document work experience with detailed job descriptions
-
☐ Research approved credential evaluation services (if applicable)
-
☐ Create backup documentation storage system
Application Phase:
-
☐ Complete certification body membership requirements
-
☐ Submit official transcripts directly from institutions
-
☐ Provide work experience verification letters
-
☐ Pay application and examination fees
-
☐ Schedule examination dates strategically
-
☐ Set up study timeline with milestone markers
Post-Certification Phase:
-
☐ Register for continuing education requirements
-
☐ Update professional profiles and resumes
-
☐ Negotiate salary adjustments with current employer
-
☐ Explore specialized career opportunities
-
☐ Maintain professional association memberships
-
☐ Plan certification renewal timeline
David discovered his bachelor’s degree from a regional university wasn’t being recognized by his chosen certification body due to accreditation issues. Rather than switching programs, he enrolled in additional coursework at an accredited institution to supplement his credentials. This strategic approach allowed him to maintain his certification timeline while strengthening his educational foundation, ultimately leading to acceptance and successful certification completion.
The comprehensive approach outlined in this guide transforms CMA certification from a simple credentialing exercise into a strategic career development initiative. By addressing documentation challenges proactively, leveraging emerging technologies, and understanding the complete economic ecosystem, you position yourself for sustained professional growth that extends far beyond the initial certification achievement.